Master Class 10 Maths Unit 3: Growth and Depreciation – Complete Guide & Exercises
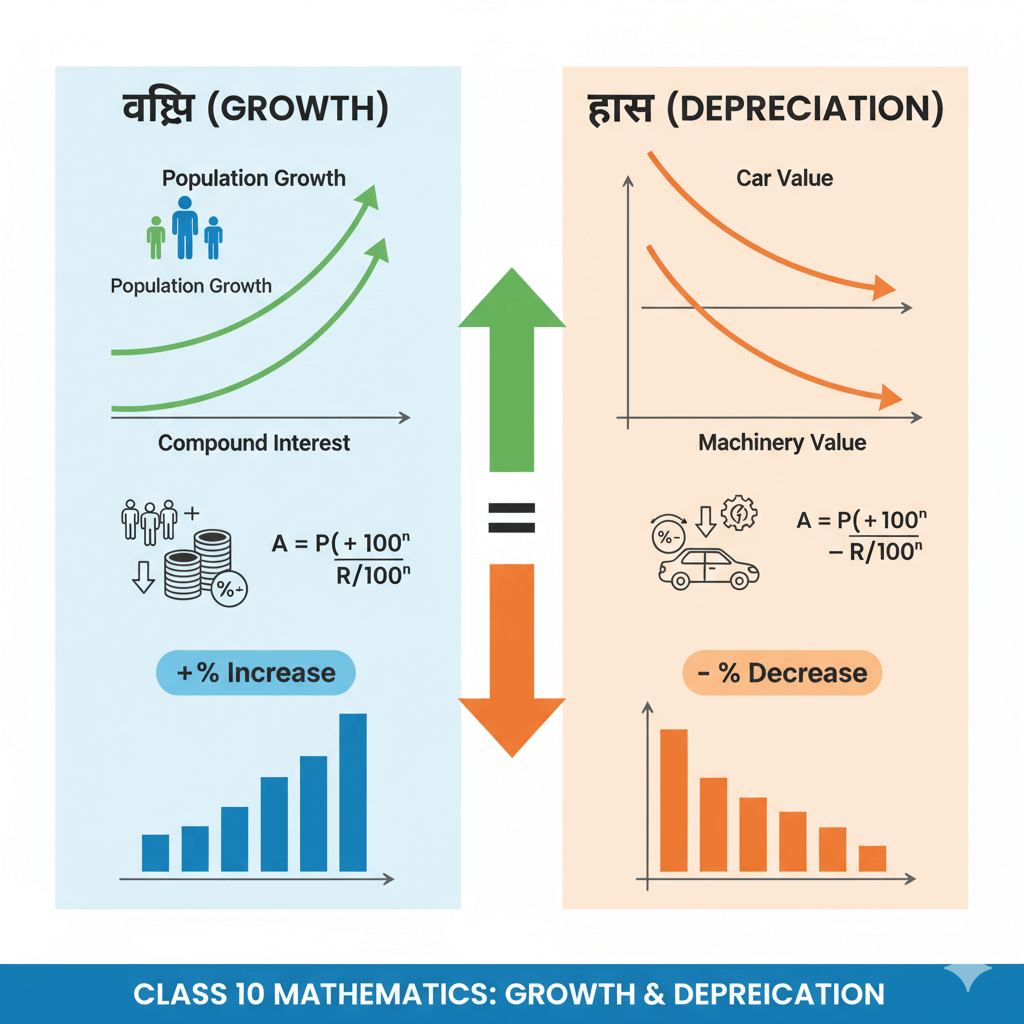
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on Class 10 Maths Unit 3: Growth and Depreciation. This essential chapter introduces students to practical mathematical concepts that have real-world applications in finance, economics, and business. Understanding growth and depreciation is crucial for solving problems related to population growth, compound interest, asset value reduction, and more.
In this detailed post, we’ll explore all aspects of Class 10 Maths Unit 3 Growth and Depreciation, including key concepts, formulas, solved examples, and practice exercises. Whether you’re preparing for exams or simply want to strengthen your mathematical skills, this guide will provide everything you need to master this important topic.
Understanding Growth and Depreciation in Class 10 Maths
The concepts of growth and depreciation in Class 10 Maths Unit 3 revolve around calculating how values change over time. Growth refers to the increase in value of something, such as population, money, or investments. Depreciation, on the other hand, describes the decrease in value of assets like vehicles, machinery, or property over time.
Key Formulas in Growth and Depreciation
To solve problems in Class 10 Maths Unit 3 Growth and Depreciation, you need to understand and apply these fundamental formulas:
Important Formulas to Remember
Growth Formula: A = P(1 + r/100)n
Depreciation Formula: A = P(1 – r/100)n
Where:
A = Final amount
P = Principal or initial amount
r = Rate of growth or depreciation
n = Time period
Types of Problems in Class 10 Maths Unit 3
In Class 10 Maths Unit 3 Growth and Depreciation, you’ll encounter various problem types:
- Population growth calculations
- Compound interest problems
- Depreciation of assets
- Comparison of simple and compound growth
- Finding original values from depreciated amounts
Solved Examples from Class 10 Maths Unit 3 Growth and Depreciation
Let’s work through some typical problems you might encounter in Class 10 Maths Unit 3 Growth and Depreciation:
Example 1: Population Growth
The population of a town increases by 5% annually. If the current population is 20,000, what will be the population after 3 years?
Solution:
Using the growth formula: A = P(1 + r/100)n
A = 20000(1 + 5/100)3
A = 20000(1.05)3
A = 20000 × 1.157625 = 23,152.5 ≈ 23,153
Therefore, the population after 3 years will be approximately 23,153.
Example 2: Asset Depreciation
A machine worth ₹50,000 depreciates at 10% per annum. What will be its value after 4 years?
Solution:
Using the depreciation formula: A = P(1 – r/100)n
A = 50000(1 – 10/100)4
A = 50000(0.9)4
A = 50000 × 0.6561 = ₹32,805
Therefore, the value of the machine after 4 years will be ₹32,805.
Exam Tip
When solving Class 10 Maths Unit 3 Growth and Depreciation problems, always double-check whether you should use the growth formula (for increases) or depreciation formula (for decreases). Mixing these up is a common mistake!
Practice Exercises for Class 10 Maths Unit 3 Growth and Depreciation
Now that we’ve covered the concepts and formulas, it’s time to practice with exercises specifically designed for Class 10 Maths Unit 3 Growth and Depreciation:
Additional Practice Problems
Try solving these additional problems to strengthen your understanding of Class 10 Maths Unit 3 Growth and Depreciation:
- The value of a car depreciates at 15% per annum. If its present value is ₹6,25,000, what was its value 2 years ago?
- A population grows from 50,000 to 60,000 in 3 years. What is the annual growth rate?
- An investment of ₹10,000 grows at 8% compound interest. What will be its value after 5 years?
- A machine costing ₹80,000 depreciates to ₹58,320 in 2 years. Find the rate of depreciation.
Additional Resources for Class 10 Maths Unit 3
Enhance your understanding of Class 10 Maths Unit 3 Growth and Depreciation with these valuable resources:
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Class 10 Maths Unit 3
When studying Class 10 Maths Unit 3 Growth and Depreciation, students often make these common errors:
- Using simple interest formula instead of compound interest for growth problems
- Forgetting to convert percentage rates to decimals in calculations
- Mixing up growth and depreciation formulas
- Not reading problems carefully to identify whether it’s a growth or depreciation scenario
- Rounding off intermediate values too early, leading to inaccurate final answers
Pro Tip for Exam Success
Create a formula sheet specifically for Class 10 Maths Unit 3 Growth and Depreciation and practice applying these formulas to different problem types. Time yourself while solving problems to improve your speed and accuracy for exams.
Conclusion: Mastering Class 10 Maths Unit 3 Growth and Depreciation
Understanding Class 10 Maths Unit 3 Growth and Depreciation is essential not only for academic success but also for practical life applications. These mathematical concepts help us make informed decisions about investments, understand economic trends, and calculate asset values over time.
By thoroughly studying the formulas, practicing with various problem types, and utilizing the resources provided in this guide, you’ll be well-prepared to excel in this important chapter. Remember to review the solved examples, attempt all practice exercises, and don’t hesitate to revisit concepts that need reinforcement.
For more educational resources and guides on Class 10 Maths Unit 3 Growth and Depreciation and other subjects, explore our website’s comprehensive learning materials designed specifically for English medium students.
