Master Class 10 Maths Unit 5: Area and Volume – Essential Guide & Practice Exercises
Class 10 Maths Unit 5 Area and Volume is one of the most practical and essential chapters in the mathematics curriculum. This comprehensive guide will help you master all the concepts, formulas, and problem-solving techniques needed to excel in this unit. Understanding area and volume calculations is crucial not only for academic success but also for real-world applications in fields like architecture, engineering, and design.
In this detailed post, we’ll explore everything about Class 10 Maths Unit 5 Area and Volume, from basic concepts to advanced problem-solving strategies. We’ve included comprehensive explanations, solved examples, and practice exercises to ensure you have all the resources needed to master this important topic.
Understanding Class 10 Maths Unit 5 Area and Volume Concepts
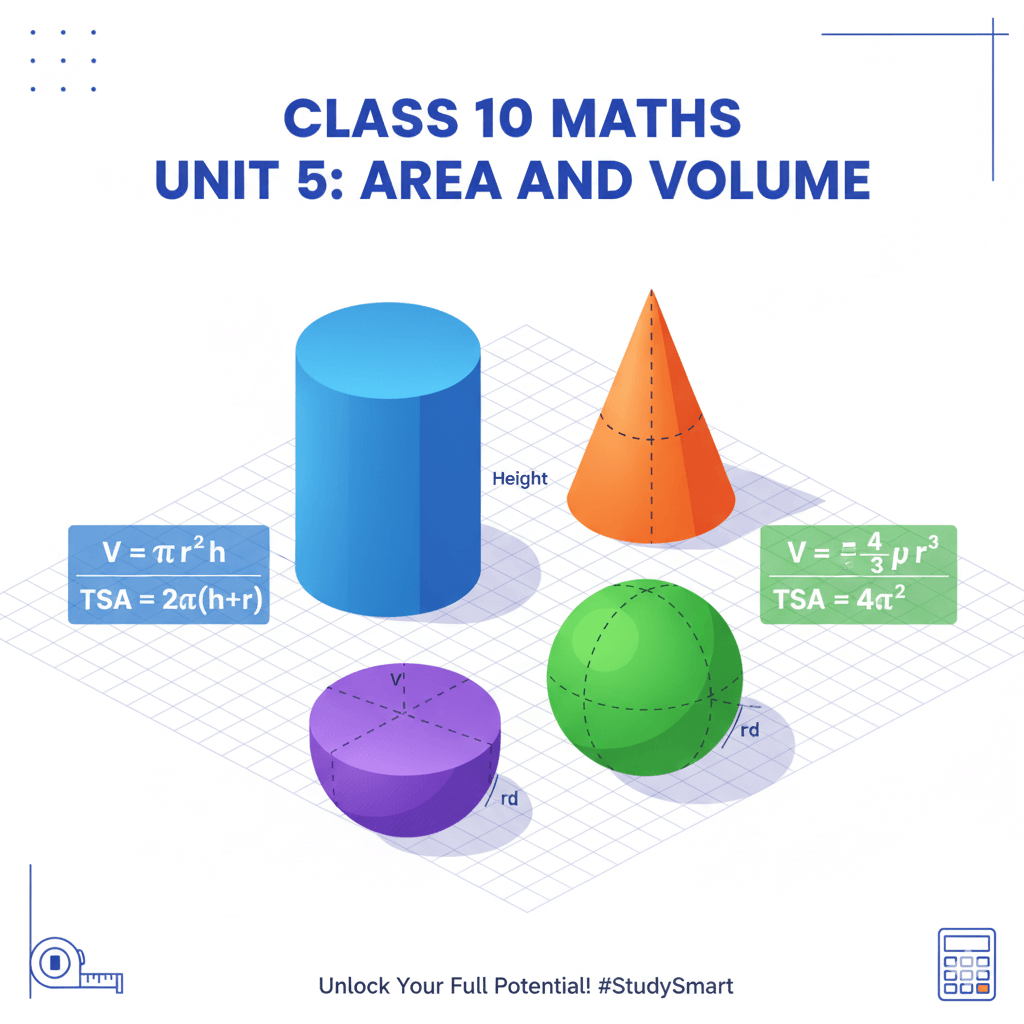
The Class 10 Maths Unit 5 Area and Volume chapter covers the calculation of surface areas and volumes of various solid shapes. This includes cubes, cuboids, cylinders, cones, spheres, and hemispheres. Mastering these concepts requires understanding both the formulas and their practical applications.
Essential Formulas for Class 10 Maths Unit 5 Area and Volume
To excel in Class 10 Maths Unit 5 Area and Volume, you need to memorize and understand these fundamental formulas:
| Shape | Surface Area | Volume |
|---|---|---|
| Cube | 6a² | a³ |
| Cuboid | 2(lb + bh + hl) | l × b × h |
| Cylinder | 2πr(h + r) | πr²h |
| Cone | πr(l + r) | (1/3)πr²h |
| Sphere | 4πr² | (4/3)πr³ |
| Hemisphere | 3πr² | (2/3)πr³ |
Important Note: Formula Memorization
For Class 10 Maths Unit 5 Area and Volume, create flashcards with these formulas and practice regularly. Understanding the derivation of these formulas will help you remember them better and apply them correctly in different problem scenarios.
Key Concepts in Class 10 Maths Unit 5 Area and Volume
When studying Class 10 Maths Unit 5 Area and Volume, focus on these essential concepts:
- Difference between total surface area and lateral surface area
- Conversion between different units of measurement
- Application of Pythagoras theorem in finding heights and slant heights
- Problems involving combination of solids
- Real-world application problems
Solved Examples from Class 10 Maths Unit 5 Area and Volume
Let’s work through some typical problems you might encounter in Class 10 Maths Unit 5 Area and Volume:
Example 1: Cylinder Volume and Surface Area
A cylindrical container has a radius of 7 cm and height of 15 cm. Find its volume and total surface area.
Solution:
Volume of cylinder = πr²h
= (22/7) × 7² × 15
= (22/7) × 49 × 15
= 22 × 7 × 15 = 2310 cm³
Total surface area = 2πr(h + r)
= 2 × (22/7) × 7 × (15 + 7)
= 2 × 22 × 22 = 968 cm²
Example 2: Cone Problems
A cone has a radius of 6 cm and slant height of 10 cm. Find its height, curved surface area, and volume.
Solution:
Using Pythagoras theorem: h² = l² – r²
h² = 10² – 6² = 100 – 36 = 64
h = √64 = 8 cm
Curved surface area = πrl
= (22/7) × 6 × 10
= (22/7) × 60 ≈ 188.57 cm²
Volume = (1/3)πr²h
= (1/3) × (22/7) × 6² × 8
= (1/3) × (22/7) × 36 × 8
= (1/3) × (22/7) × 288 ≈ 301.71 cm³
Exam Strategy
When solving Class 10 Maths Unit 5 Area and Volume problems, always write down the known values first, then select the appropriate formula. Double-check your units and ensure your final answer makes logical sense in the context of the problem.
Practice Exercises for Class 10 Maths Unit 5 Area and Volume
Now that we’ve covered the concepts and formulas, it’s time to practice with exercises specifically designed for Class 10 Maths Unit 5 Area and Volume:
Additional Practice Problems
Try solving these additional problems to strengthen your understanding of Class 10 Maths Unit 5 Area and Volume:
- A cuboidal water tank is 6 m long, 5 m wide, and 4.5 m deep. How many liters of water can it hold?
- The diameter of a sphere is 14 cm. Find its surface area and volume.
- A hemispherical bowl has a radius of 3.5 cm. What would be the volume of water it could contain?
- A right circular cone has a height of 12 cm and base radius of 5 cm. Find its slant height and total surface area.
Additional Resources for Class 10 Maths Unit 5
Enhance your understanding of Class 10 Maths Unit 5 Area and Volume with these valuable resources:
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Class 10 Maths Unit 5
When studying Class 10 Maths Unit 5 Area and Volume, students often make these common errors:
- Confusing lateral surface area with total surface area
- Using wrong units or forgetting to convert between units
- Applying 2D area formulas to 3D volume problems
- Miscalculating slant height in cone problems
- Forgetting to use the correct value of π (22/7 or 3.14) as required
Pro Tip for Success
Create a formula sheet specifically for Class 10 Maths Unit 5 Area and Volume and practice applying these formulas to different problem types. Draw diagrams for each problem to visualize the shapes and dimensions clearly.
Conclusion: Excel in Class 10 Maths Unit 5 Area and Volume
Mastering Class 10 Maths Unit 5 Area and Volume is essential for building a strong foundation in geometry and spatial mathematics. These concepts have practical applications in numerous fields and are frequently tested in examinations.
By thoroughly studying the formulas, practicing with various problem types, and utilizing the resources provided in this guide, you’ll be well-prepared to excel in this important chapter. Remember to practice regularly, review your mistakes, and focus on understanding the concepts rather than just memorizing formulas.
For more educational resources and guides on Class 10 Maths Unit 5 Area and Volume and other subjects, explore our website’s comprehensive learning materials designed specifically for English medium students.
